Ideal Scope
History
The
The
Light return
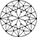
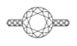
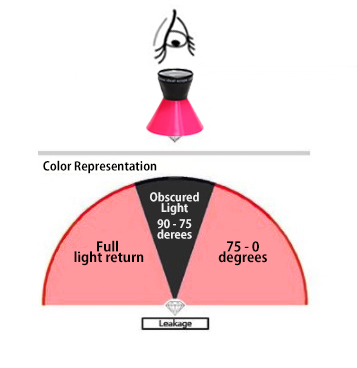
Diamond facets act like windows and mirrors, where its brightness comes from the reflection of the light source to your eyes. Thus, the redder the Ideal scope image, the brighter the diamond.
All diamonds have some light leakages. Generally, the less light leakage the better. Light leakage would appear as white on the Ideal scope.
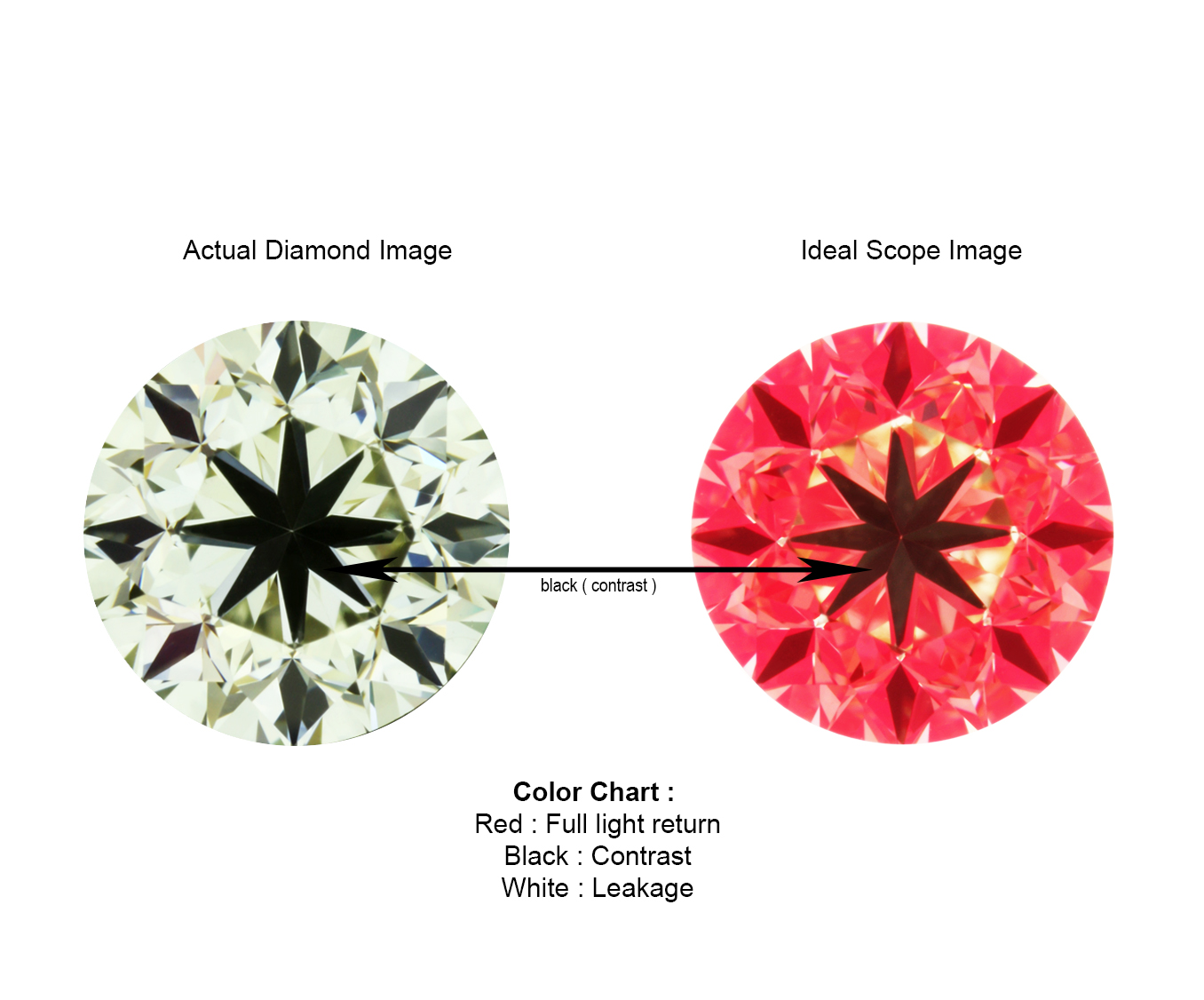
Below is an example of a Super Ideal Cut that is cut to have minimum light leakages and a well-balanced brightness and contrast which optimizes the brilliance of a diamond.
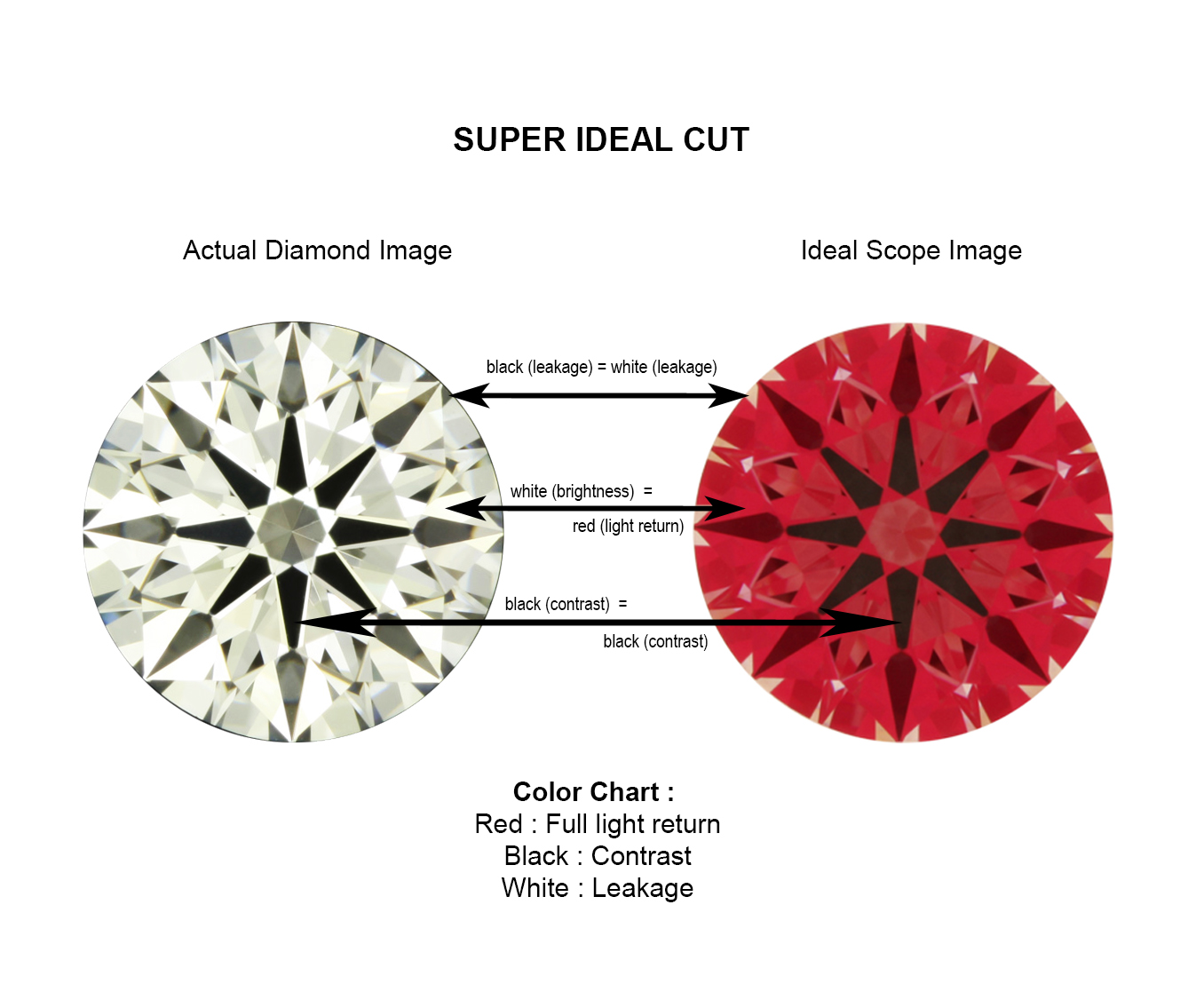
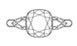
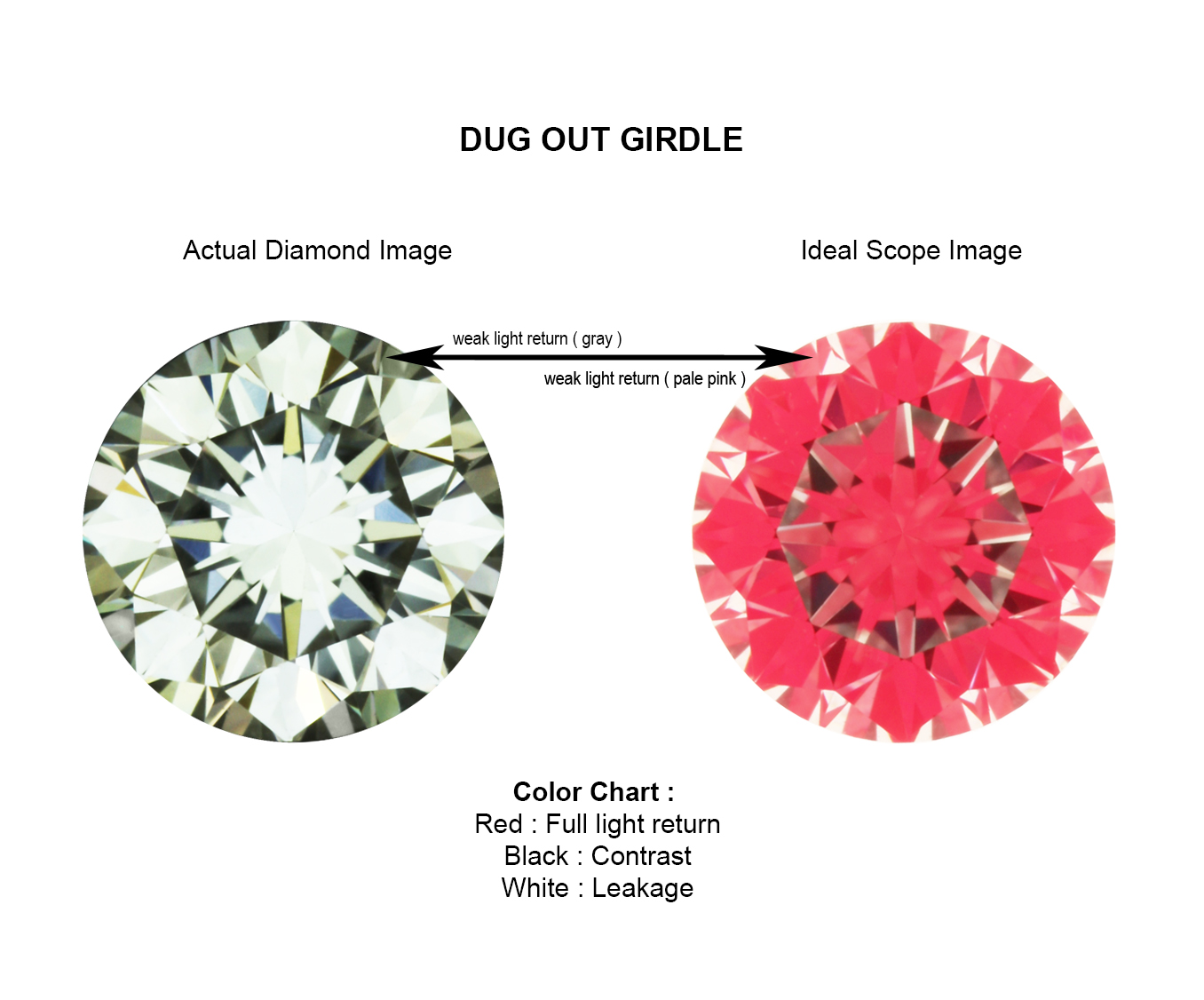
Small areas of light leakages around the girdle (edge) of a diamond add contrast to it, improving its brilliance. However, too much light leakages around the girdle (
The
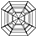
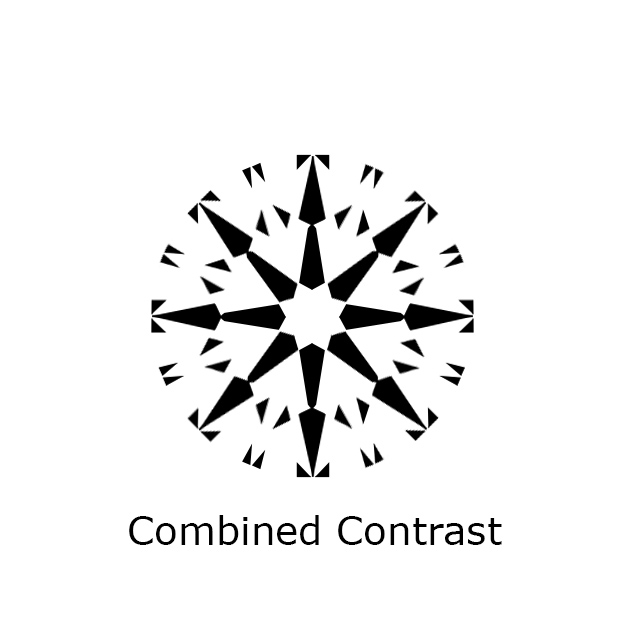
Head Shadow
The 8 distinct black arrows when you view a diamond from the front is known as the “Head Shadow Star”. It is the reflection of the observer’s head which blocks the light source. In essence, the Heart Shadow Star is the reflection of the observer’s head. It adds contrasts and sparkle, depending on the angle. Light leakages around the diamond’s girdle add contrasts on the edges of the diamond. When combined, the contrast from the Head Shadow Star and girdle light leakage create an overall contrast patterning in a diamond, improving its brilliance.


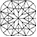
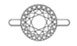
Very Shallow Cut
The diamond below shows a very shallow cut. It’s a good representation of a diamond that is over contrasted. Although this diamond has minimum light leakages, it has too much contrast, reducing the brightness as there is less red (light return) area. The over contrasted effect will cause the diamond to lose out on its brilliance despite its minimum light leakages.
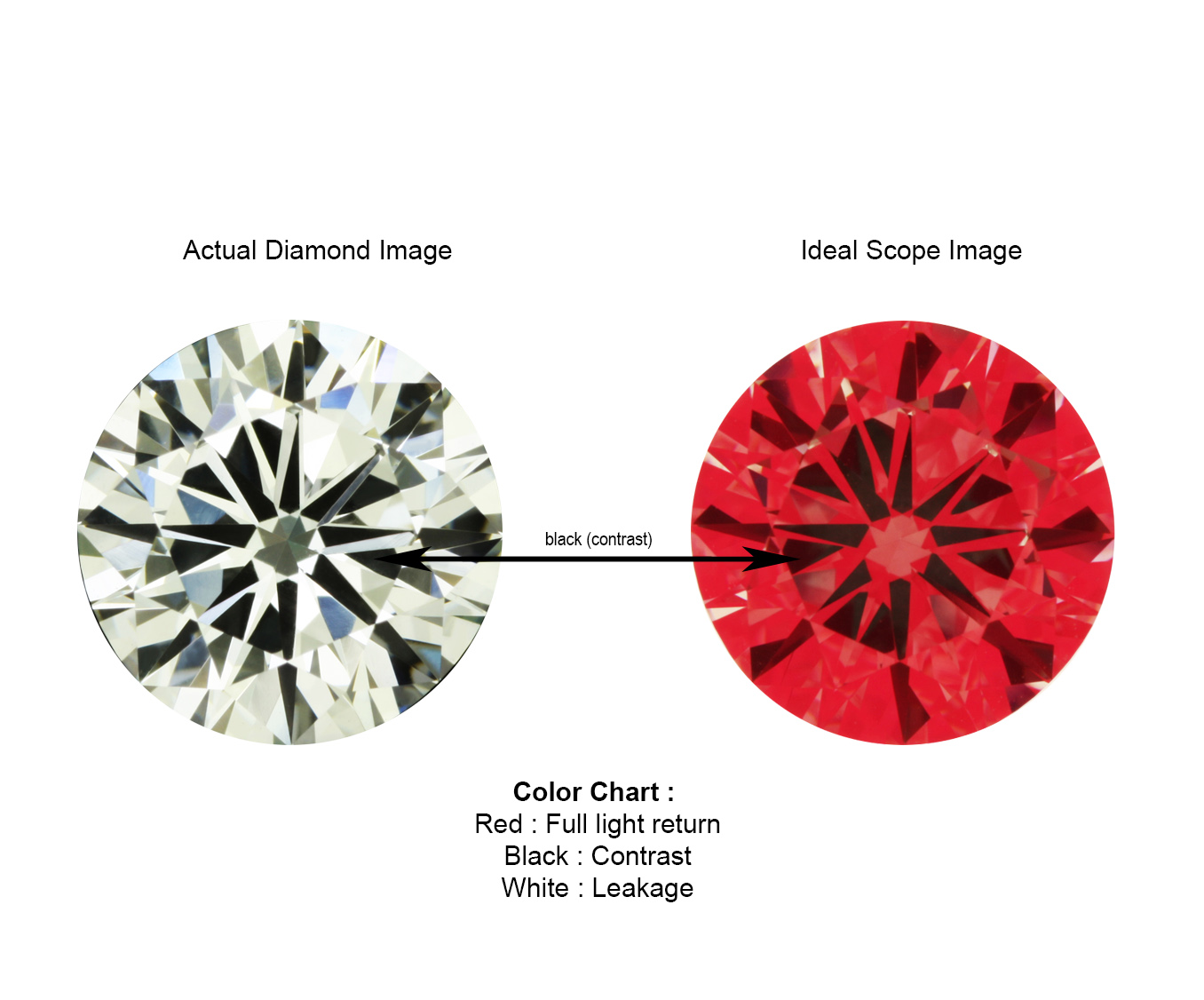
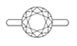
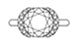
Very Deep Cut
The diamond below shows a very deep cut. It’s the opposite of the previous diamond, where it lacks contrast. The 8 black arrows are no longer contrasted, but red (light return). As a result, the 8 arrows patterning in the diamond will be hardly visible. In addition, deep cut diamonds tend to have
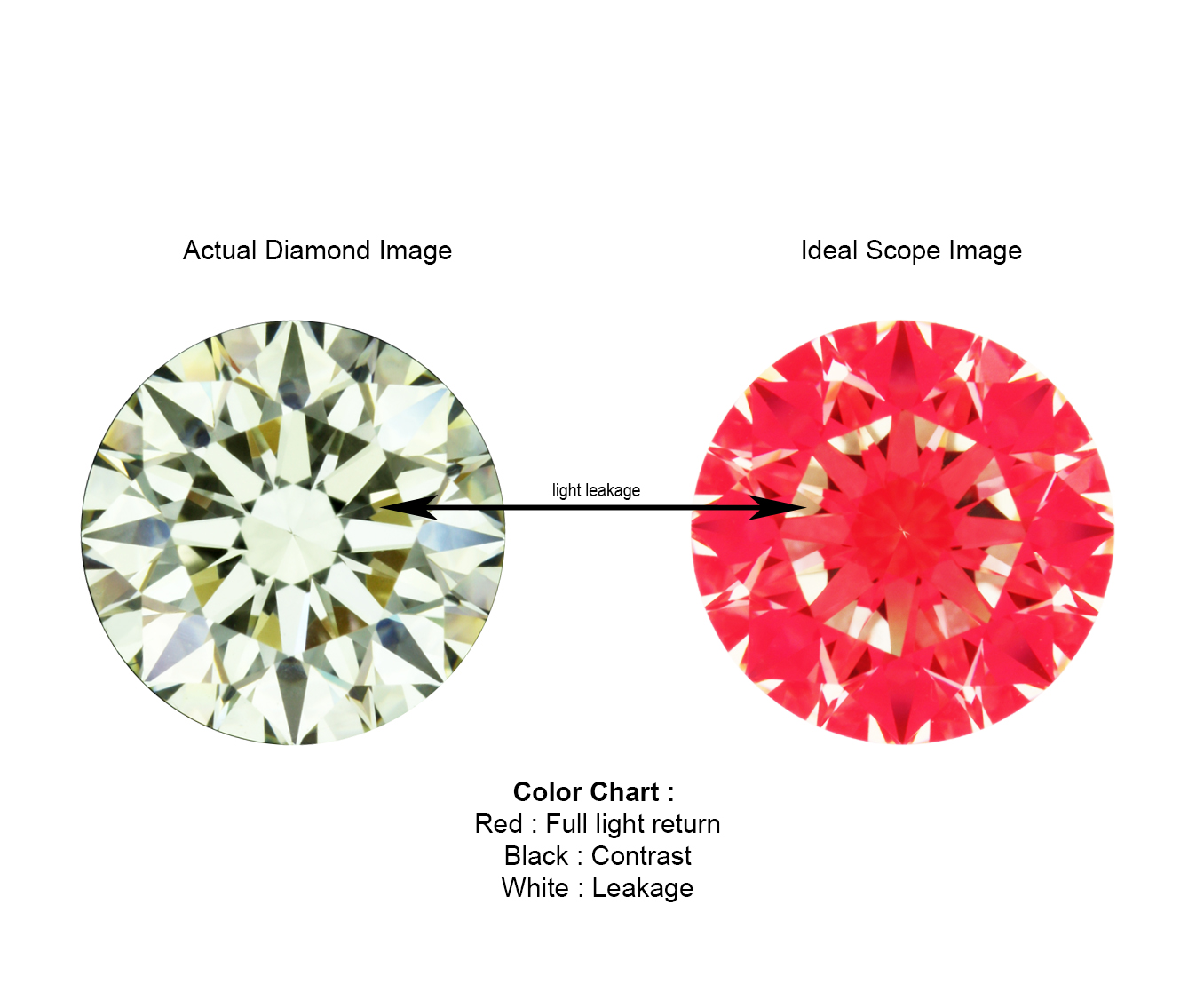
Top Heavy Diamond (high crown angle)
This image below shows a diamond with a very high crown angle, which is known as a “
This video shows both shallow and deep cut diamonds viewed under various light conditions.